Types of Camera Lenses: A Complete Guide

A camera lens tailored to a specific photographic need is one of the many benefits of entering the world of photography. Photographers at every level need to understand the nuances of different lens types, from capturing expansive landscapes to zooming in on distant wildlife. Our comprehensive guide explores the different types of camera lenses, their unique characteristics, and when to use them.
Zoom Lenses vs. Prime Lenses:
Prime lenses and zoom lenses are the foundation of lens selection. In addition to their simplicity, prime lenses often provide superior optical quality as they have fixed focal lengths. Photographers can adjust their composition without changing lenses with zoom lenses, which provide variable focal lengths. In contrast to prime lenses, today’s zoom lenses offer high optical performance without compromising image quality, offering versatility without compromising sharpness.
Prime lenses have the following pros and cons:

When compared to zoom lenses, prime lenses excel in terms of sharpness, compactness, and affordability. They require frequent lens changes for framing adjustments, so photographers must anticipate their shooting needs in advance.
Normal lenses have the following roles:

The perspective of the human eye is reflected by the normal lens, which typically has a focal length of 50mm. These cameras are versatile and well-suited to various shooting scenarios, capturing natural-looking scenes that are indispensable for everyday photography.
Zoom lenses are versatile in the following ways:
With zoom lenses, you can adjust focal lengths within one lens, eliminating the need to change lenses frequently. Photographers can benefit from zoom lenses’ adaptability without compromising image quality when time or space constraints make lens swaps impractical.
Lenses in Kits: An Introduction

With kit lenses, beginners can explore different photographic genres with a variety of focal ranges available with entry-level cameras. Despite their lack of build quality and maximum aperture, these lenses are a good place to start learning photography basics.
The advantages and limitations of superzoom lenses are as follows:
Having a wide focal range, superzoom lenses can be used in a variety of shooting scenarios. However, their ambitious zoom range might compromise image quality, necessitating a balance between versatility and optical quality.
A wide-angle lens’ exploration:

The wide-angle lens captures expansive scenes, making it ideal for landscapes and architectural photography. By enhancing depth of field and adding creative distortion effects, they allow photographers to create compositions that are visually compelling.
An introduction to ultra wide-angle lenses:
Landscapes and architecture are viewed with dramatic perspective when using ultra wide-angle lenses. There are rectilinear and fisheye lenses available to suit a variety of creative needs, whether they are used to capture straight lines or make use of intentional distortion to create an artistic effect.
Lenses with telephoto capabilities are used in the following applications:

Photographers use telephoto lenses to capture distant subjects, making them indispensable for wildlife, sports, and portraits. Using their compressed perspective and shallow depth of field, photographers can bring distant scenes closer with clarity and detail.
What you need to know about super-telephoto lenses:
Besides telephoto ranges, super-telephoto lenses provide specialized capabilities for shooting extreme wildlife or astrophotography. Despite their exceptional reach, they are large, heavy, and costly, making them an investment for professionals.
Teleconverters perform the following functions:
Although teleconverters are cost-effective for extending the reach of telephoto lenses, they degrade image quality and light transmission. Despite these limitations, they offer photographers more flexibility when capturing distant subjects.
Macro Lens Exploration:
With macro lenses, you can capture close-up images of small objects with great magnificence and sharpness. Photographers can capture the beauty of nature or explore product photography at a micro level with them.
Rectilinear and Fisheye Lenses Explained:

For realistic perspectives, rectilinear lenses maintain straight lines in the scene. To create artistic expression and immersive storytelling, fisheye lenses intentionally distort images, creating curved lines and exaggerated angles.
Tilt-Shift Lenses: An Introduction:
Photographers can manipulate depth of field and perspective using tilt-shift lenses, which may be particularly useful for architectural photography. The tilting and shifting of lens elements can be used by photographers to correct perspective distortion and achieve selective focus in a creative and precise manner.
Selection of lenses should be based on the following factors:
Choosing lenses is a matter of balancing photographers’ specific needs with their budgetary limitations. Creative and skill remain more important than equipment when it comes to capturing memorable photographs.
Lenses have the following significance:
Photographers consider lenses to be the most crucial piece of equipment, determining what type of pictures they will be able to take. For visual storytelling, lenses serve as indispensable tools for controlling perspective, depth of field, and image quality.
Lens Anatomy:
There are several components that make up a modern lens, including the filter thread, the front element, the zoom ring, the focus ring, and various switches. In order to maximize lens performance, photographers must understand its anatomy.
The following terms are used to describe camera lenses:
There are standardized formats for lens names that include the brands, the type, the focal length, the maximum aperture, and other features. It is crucial to understand the focal length and aperture of a lens before choosing it to be the best tool for the job.
Focus Length and Its Impact:
With prime lenses offering fixed focal lengths and zoom lenses offering variable focal lengths, a lens’ field of view and magnification are determined by its focal length. In addition to expanding photographers’ creative horizons, specialty lenses serve unique purposes.
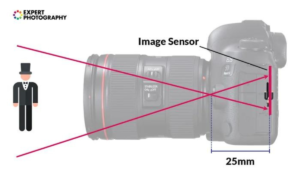
The impact of the camera sensor is as follows:
A camera’s sensor size affects the apparent focal length of a lens, affecting the field of view and depth of field. Composition and framing must be adjusted when using smaller sensors with the same focal length.
Maximal Aperture:
An f-number represents the maximum aperture of a lens, which affects the amount of light it can collect and the depth of field it can produce. Portrait and still life photographers benefit from prime lenses’ larger maximum apertures, which offer better low-light performance and greater background blur control.
The depth of field is:
Similarly, maximum aperture affects depth of field, with larger apertures producing shallower focus effects for isolating subjects. With a deeper understanding of depth of field, photographers can create images with a greater visual impact by controlling focus and composition.
Zooms with variable aperture:

Depending on the focal length, some zoom lenses have variable maximum apertures. However, these lenses have limitations in low-light situations or when seeking consistent exposure across zoom ranges despite their cost and size advantages.
Lens features include:
There are several factors that influence the lens selection process, such as size, weight, autofocus performance, durability, and weather sealing, as well as image quality concerns. The best results are achieved when a lens is chosen based on the individual’s preferences and shooting requirements.
Quality of image captured by lens:
Focus shift and astigmatism are specialized concerns that influence the quality of an image, while sharpness, distortion and chromatic aberration have a significant influence on it. A photographer’s ability to discern subtle nuances and make informed decisions is enhanced by evaluating lenses in real-world scenarios.
Comparing third-party and name-brand lenses:
Often at a lower price point, third-party lenses provide a competitive alternative to name-brand counterparts. Third-party lenses offer comparable quality and performance, extending options for photographers across budgets despite concerns about autofocus performance and compatibility.
The conclusion is:
For photographers seeking to elevate their craft, understanding camera lenses is crucial. In order to improve the quality and versatility of their photographic endeavors, photographers should familiarize themselves with different lens types, features, and terminology. In capturing compelling images that resonate with audiences, lenses are essential tools, but creativity and skill remain crucial.



